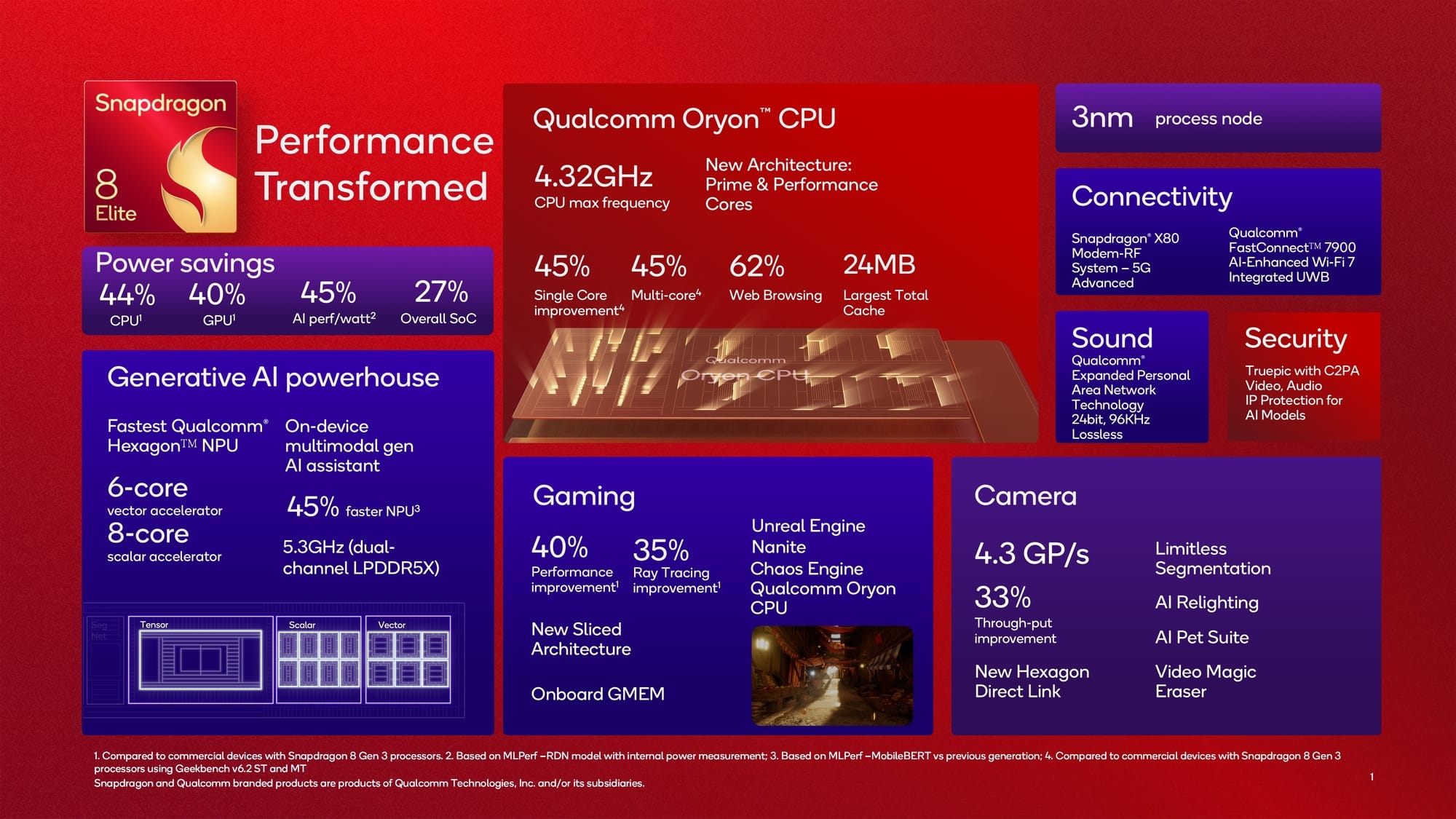
The Snapdragon 8 Elite features Qualcomm's custom Oryon CPU and AI ISP. Here's everything you need to know.


Back in early 2021, Qualcomm acquired Nuvia, a promising startup founded by former Apple and Google semiconductor design engineers. Nuvia was designing high-performance, custom Arm-based CPUs for servers before it was acquired by Qualcomm, who later used that IP to create the custom Oryon CPU cores in the Snapdragon X Elite chip powering the initial slate of Copilot+ PCs. Now, Qualcomm is bringing its custom Oryon CPU to its mobile lineup, starting with the new Snapdragon 8 Elite.
The Snapdragon 8 Elite, Qualcomm says, is not just an upgrade over the Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 but a "quantum leap forward." That's why the new chip is named the Snapdragon 8 Elite instead of the Snapdragon 8 Gen 4 as everyone expected; the Snapdragon Elite name is Qualcomm's branding for its most advanced products.
The 8 Elite has Qualcomm's fastest-ever CPU for a mobile device, supports the latest graphics engine features, is ready for on-device multimodal generative AI, can handle complex AI image and video processing algorithms entirely on-device, supports the most advanced connectivity features, and is fabricated using TSMC's N3E (3nm) processing node. Here's everything you need to know about Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Elite.
With the Snapdragon 8 Elite, Qualcomm is finally adopting an "all big core" CPU configuration, like the MediaTek Dimensity 9300 and 9400. That means the Snapdragon 8 Elite doesn't have any lower-end "efficiency" cores, which you might think is bad for power efficiency but has actually proven to be the opposite. Faster CPUs can finish tasks more quickly, which means those CPUs can also return to idle or shut down more quickly.
The Snapdragon 8 Elite has an octa-core CPU consisting of 2 "Prime" cores clocked at up to 4.32GHz and 6 "Performance" cores clocked at up to 3.53GHz. These 6 "Performance" cores have been tuned to run intensive apps while being power efficient. All 8 CPU cores are based on Qualcomm's second-generation Oryon microarchitecture, which the company says is not plug and play from its Snapdragon X Elite chip but rather a brand new microarchitecture that's up to 46% more efficient. What's more, Qualcomm says its new CPU is the fastest in the mobile industry, offering an up to 50% CPU performance uplift compared to the last-generation 8 Gen 3.
Qualcomm has paired these cores with a large amount of cache, 12MB of L2 cache for the "Prime" cluster and 12MB of L2 cache for the "Performance" cluster for a total of 24MB. It also upped the L1 cache within each core to 192KB for the "Prime" cores and 128KB for the "Performance" cores.
The memory controller, meanwhile, supports LPDDR5X RAM modules clocked at up to 5.3GHz.

Finally, Qualcomm talked briefly about one of the optimizations it made to enhance performance in mobile workloads. The company is introducing a new data cache prefetcher. Qualcomm says it wanted to solve the issue of frequent power cycling of individual cores, so it developed a feature called instant wake. The company says it eliminated the need for a reset code to be sent to prepare a core that's powering up to execute the next operation; thanks to new hardware, the core that's powering up can execute the next instruction immediately.
The Snapdragon 8 Elite features Qualcomm's newest custom Adreno GPU along with support for the latest Unreal Engine 5 features. These include support for Unreal Engine's Chaos Physics system, a physics simulation and destruction system, and Nanite, a virtualized geometry system. Qualcomm says its Oryon CPU cores can render over 9,000 unique physics objects in a render environment, all while handling the processing, destruction, and collision of over 1,000 objects with less than 5ms of latency. With support for Nanite, Qualcomm says its Snapdragon 8 Elite can render "film-quality 3D environments" thanks to the massive increase in geometric complexity that Nanite offers.
Qualcomm hasn't revealed many details about its latest Adreno GPU, though it did mention it features its first-ever "sliced architecture." There are three GPU slices, each clocked at up to 1.1GHz, that are "fine-tuned for modern graphics workloads." Each slice is an independent shader processor-based core, allowing for better work distribution and concurrency. When the GPU is rendering complex scenes, Qualcomm says it can store up to 12MB of data directly, thus sending less graphical data to DDR memory. Overall, Qualcomm says these improvements result in higher clock speeds, better frame rates, sharper images, and longer sustained gameplay sessions.
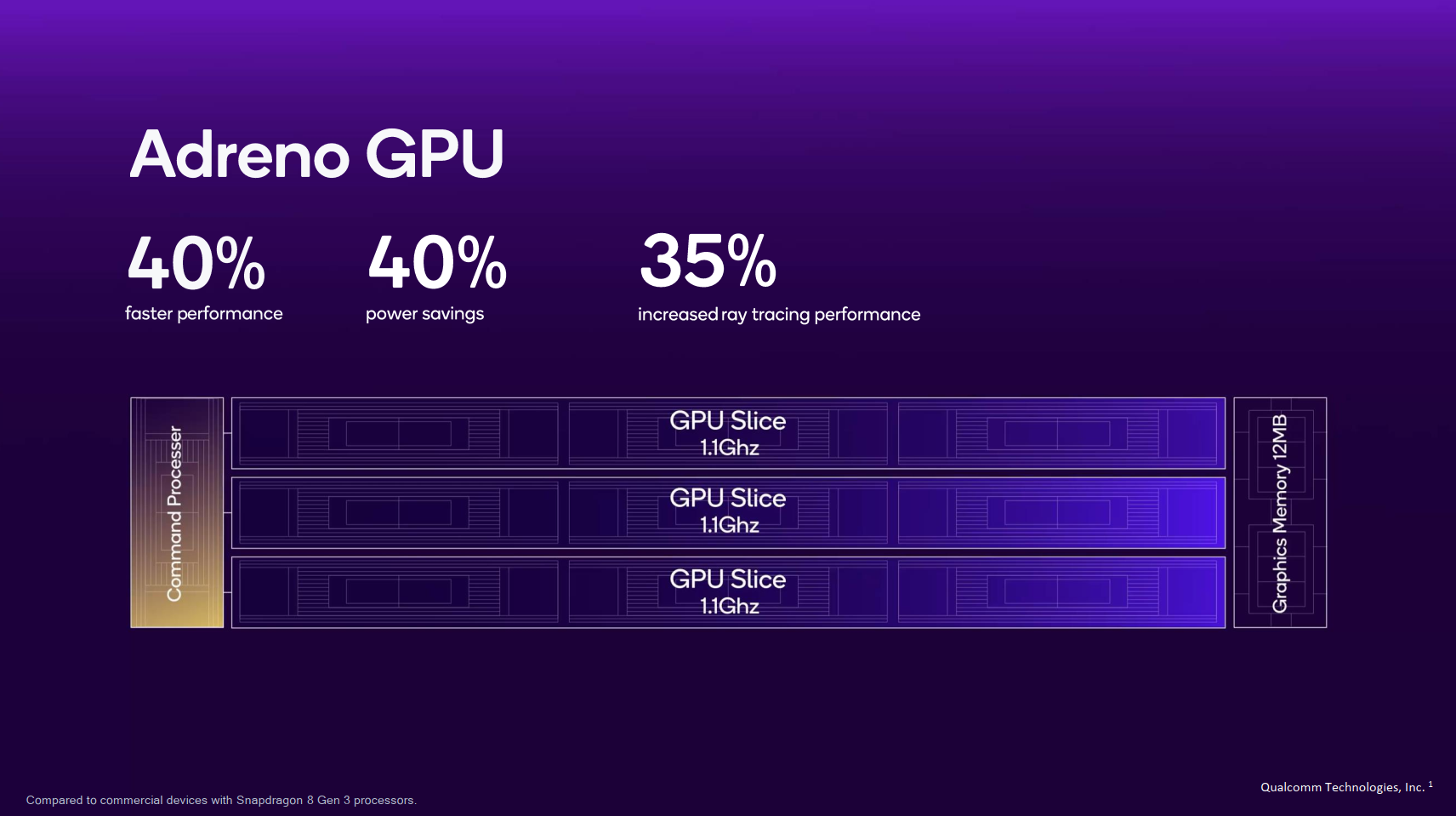
Specifically, the company says its Snapdragon 8 Elite offers 40% better power efficiency versus the Snapdragon 8 Gen 3, resulting in gaming sessions that last 2.5 hours longer. It also offers 40% improved GPU performance, 35% increased ray-tracing performance, and 40% reduced memory read bandwidth.
To showcase these improvements, Qualcomm says it worked with a few mobile game development companies to optimize their games for the new chipset. Feral Interactive's upcoming mobile launch of GRID Legends, for example, uses Qualcomm's Adaptive Performance Engine 4.0 to improve device power efficiency by optimizing game thread schedules.

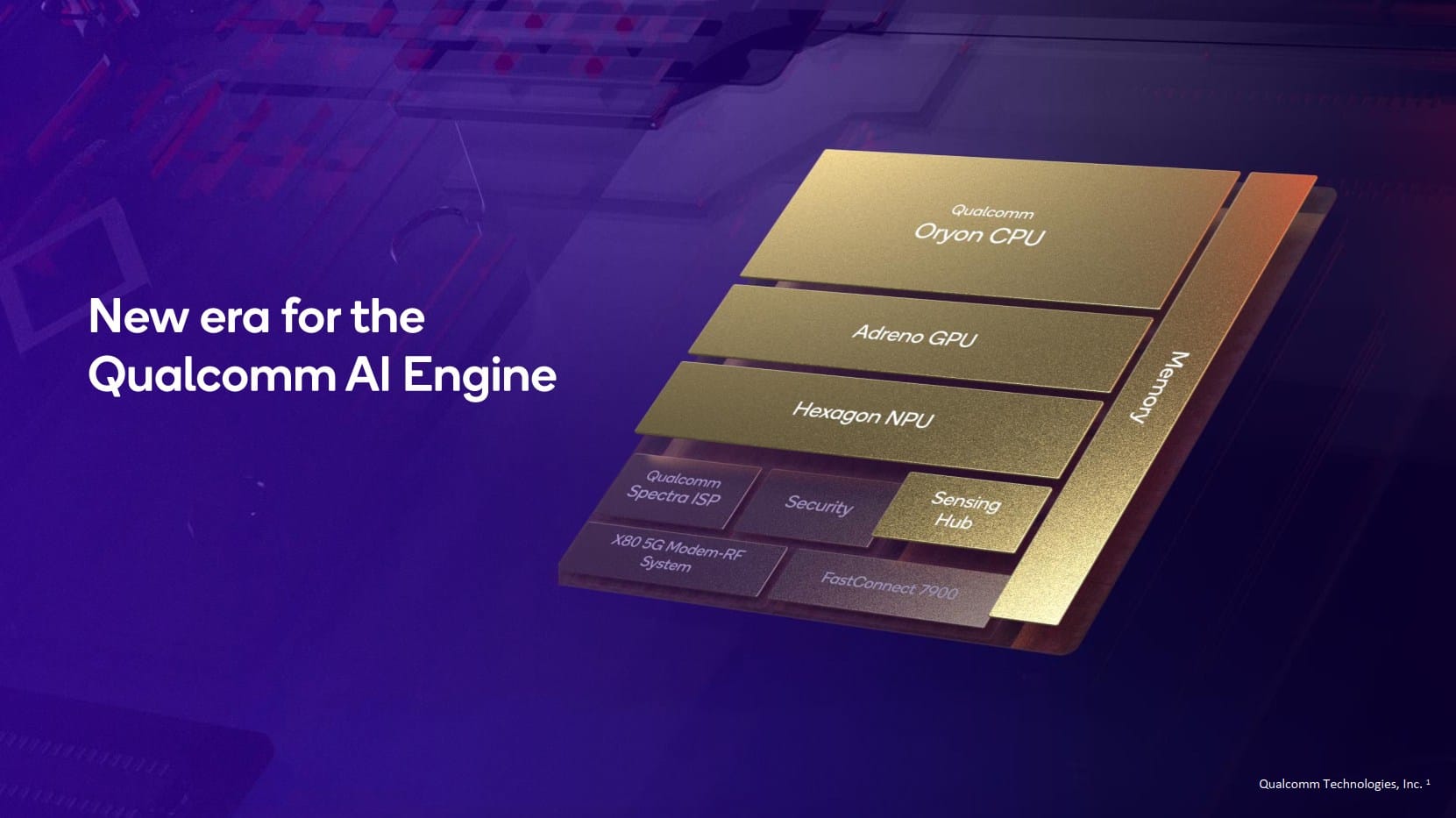
Running generative AI models on device requires very powerful and power efficient hardware, which is exactly what Qualcomm says its Snapdragon 8 Elite is equipped with. Qualcomm has made a number of improvements to its AI Engine, Hexagon NPU, and Sensing Hub to run multimodal generative AI applications entirely on-device.
Starting with the Qualcomm AI Engine, Qualcomm says it improved its FP and INT performance and that its Oryon CPU allows for ultra-low first-inference latency.
Its Hexagon NPU, meanwhile, offers up to 45% faster AI performance and better performance per watt. Qualcomm added more cores to its Scalar and Vector accelerators, for a total of 8 of the former and 6 of the latter. These added Scalar cores will improve the acceleration of LLM and classic AI models while the added Vector cores will provide longer context support. Furthermore, all cores now support higher throughput. Plus, Qualcomm says it has enhanced concurrency so AI and computer vision workloads can coexist in memory, improving flexibility and performance.
Next, the Qualcomm Sensing Hub has been upgraded with 34% more memory and 60% better AI performance. Qualcomm says the Sensing Hub is now faster and more efficient at fetching personal context data.
To demonstrate how these improvements allow for multimodal generative AI applications to be run on-device, Qualcomm showed off a multimodal AI assistant that can take text, speech, and vision inputs. Previous, non-multimodal AI assistants relied on traditional speech-to-text models to convert spoken words to text for the LLM to understand. Now, however, that step can be eliminated.
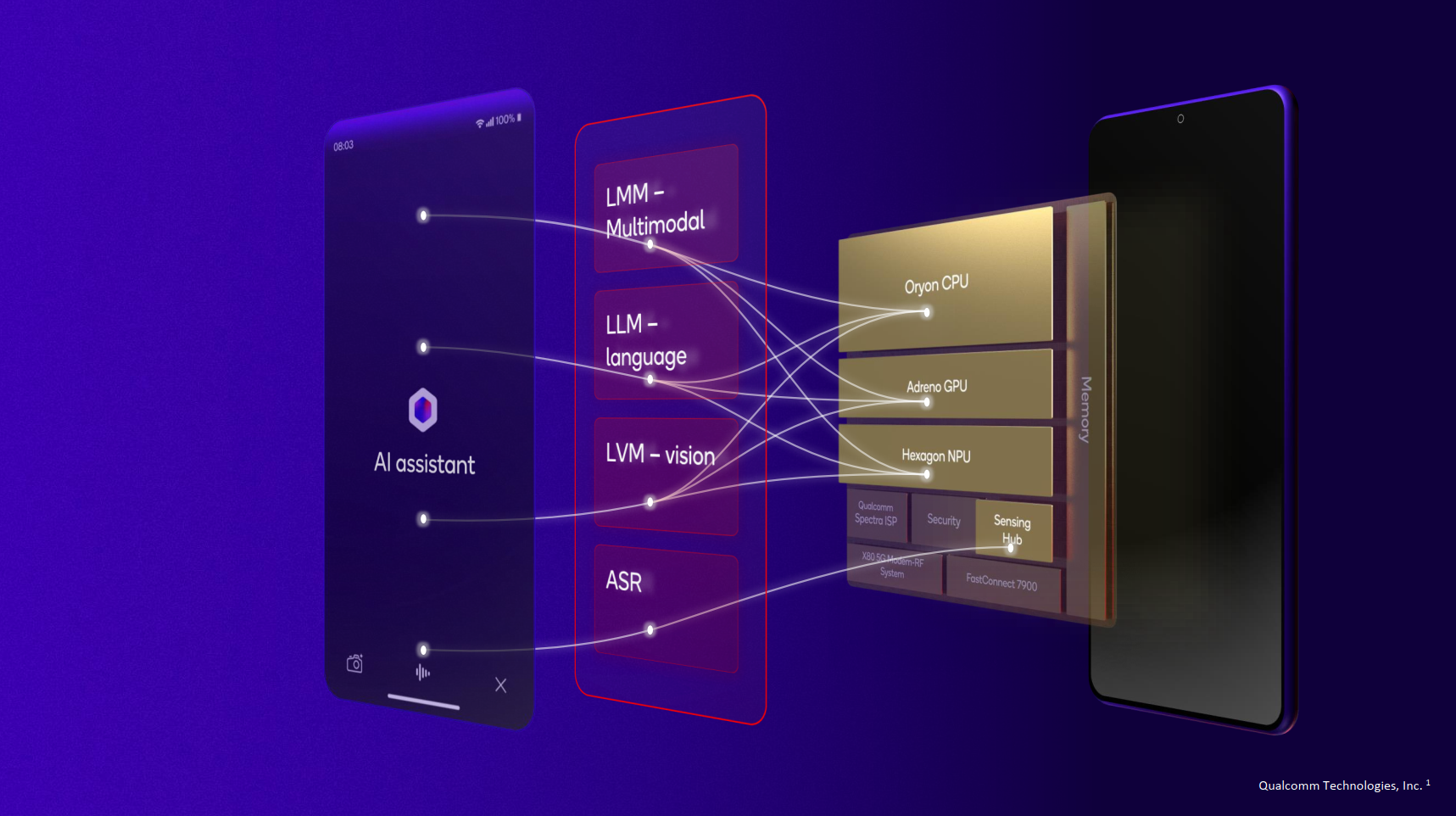
Lastly, like the MediaTek Dimensity 9400 and Google Tensor G4, the Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Elite is optimized for Google's latest multimodal Gemini Nano model.
The Image Signal Processor (ISP) in the Snapdragon 8 Elite is also getting some AI-infused upgrades along with a new name. Instead of a Spectra ISP, the Snapdragon 8 Elite has Qualcomm's AI ISP.
The Qualcomm AI ISP consists of three processors that work hand-in-hand with the Hexagon NPU. Qualcomm says it has shifted more of the image processing pipeline into the RAW domain to boost accuracy and flexibility. It has also added AI-driven enhancements to auto focus, auto exposure, and auto white balance.

The Qualcomm AI ISP in the Snapdragon 8 Elite features 35% increased pixel throughput compared to the triple cognitive Spectra ISP in the Snapdragon 8 Gen 3. By processing 4.3 gigapixels per second, the AI ISP can simultaneously process data coming in from three separate 48MP image sensors at 30fps.
Perhaps the biggest upgrade of the Qualcomm AI ISP is the overhauled Hexagon Direct Link. In the past, the ISP would process an image and then pass it to the Hexagon NPU via the Hexagon Direct Link. Now, however, the NPU can directly access native RAW sensor data, allowing for real-time AI-based enhancements to be implemented at 4K60. This allows for more accurate image and video manipulations to be achieved as well as better flexibility for OEMs that want to implement their own algorithms.
Qualcomm says its overhauled Hexagon Direct Link is what makes it possible for the Snapdragon 8 Elite to run advanced AI processing algorithms that were previously only possible to be run on cloud servers. The company is demonstrating some of these capabilities with Insight AI, a collection of AI algorithms that elevate everyday photography. With Limitless Segmentation, for example, the AI ISP can mask and identify over 250 layers in an image.


Qualcomm's Insight AI allows for "limitless" segmentation of images. Source: Qualcomm.
Afterwards, Qualcomm's Realtime Skin and Sky algorithms can recognize and correct lighting conditions to capture natural skintones and true-to-life sky colors. This can be used to implement real-time relighting during video calls so your face appears natural and well-lit even with tricky backlighting.
Qualcomm also says that capabilities like object removal from videos is now possible using its AI ISP. Object removal on mobile devices is currently something that can only be done on static images.
To cap things off, the Snapdragon 8 Elite supports all the latest connectivity features thanks to its integrated Snapdragon X80 modem and optional FastConnect 7900 connectivity chip.
The Snapdragon X80 is Qualcomm's seventh-generation 5G modem-RF system and its first with fully integrated NB-NTN (narrowband non-terrestrial network) satellite communications support, a 6-antenna architecture for smartphones, and 6X carrier aggregation. Qualcomm says the X80 has a tensor accelerator to power a few “AI” features, such as AI-based mmWave range extension which extends the range for fixed-wireless access applications. Other improvements include a 30% boost in location accuracy, reduction of 20% for best-cell selection time, 30% faster link acquisition, and 60% faster CPE service acquisition for mmWave connections.
The FastConnect 7900 is Qualcomm's latest flagship connectivity chip for mobile devices. It notably integrates Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and UWB into a single chip. Previous iterations of the FastConnect chip did not include UWB, so OEMs had to either use a different chip entirely or embed a separate UWB module.
The FastConnect 7900 supports advanced features like Bluetooth Channel Sounding, a feature of the new Bluetooth 6.0 specification that enables precise estimations of the distance between two Bluetooth devices. It also supports key Wi-Fi technologies like Wi-Fi 7 and High Band Simultaneous, but it also has some new “AI-enhanced” Wi-Fi features. Qualcomm says the chip uses AI to “understand” the context of how you’re using your Wi-Fi connection without accessing any data or doing any deep package inspections so it can optimize Wi-Fi settings to best serve what you’re doing.


Left: Summary slide of FastConnect 7900. Right: Summary slide of Snapdragon X80 5G modem-RF system.
Qualcomm says that several OEMs like ASUS, HONOR, iQOO, OnePlus, OPPO, Realme, Samsung, Vivo, Xiaomi, and others will launch devices powered by the Snapdragon 8 Elite in the coming weeks.
| Feature | |